import java.util.*;
class Node{
int data;
Node lt,rt;
public Node(int val){
data=val;
lt=rt=null;
}
}
public class BFS {
Node root;
public void BFS(Node root){
Queue<Node> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.offer(root);
int L=0;
while(!Q.isEmpty()){
int len=Q.size();
System.out.print(L+" : ");
for(int i=0; i<len;i++){
Node cur=Q.poll();
System.out.print(cur.data+" ");
if(cur.lt!=null) Q.offer(cur.lt);
if(cur.rt!=null) Q.offer(cur.rt);
}
L++;
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
BFS tree = new BFS();
tree.root=new Node(1);
tree.root.lt=new Node(2);
tree.root.rt=new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt=new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.rt=new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt=new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.rt=new Node(7);
tree.BFS(tree.root); // BFS 탐색 호출
}
}
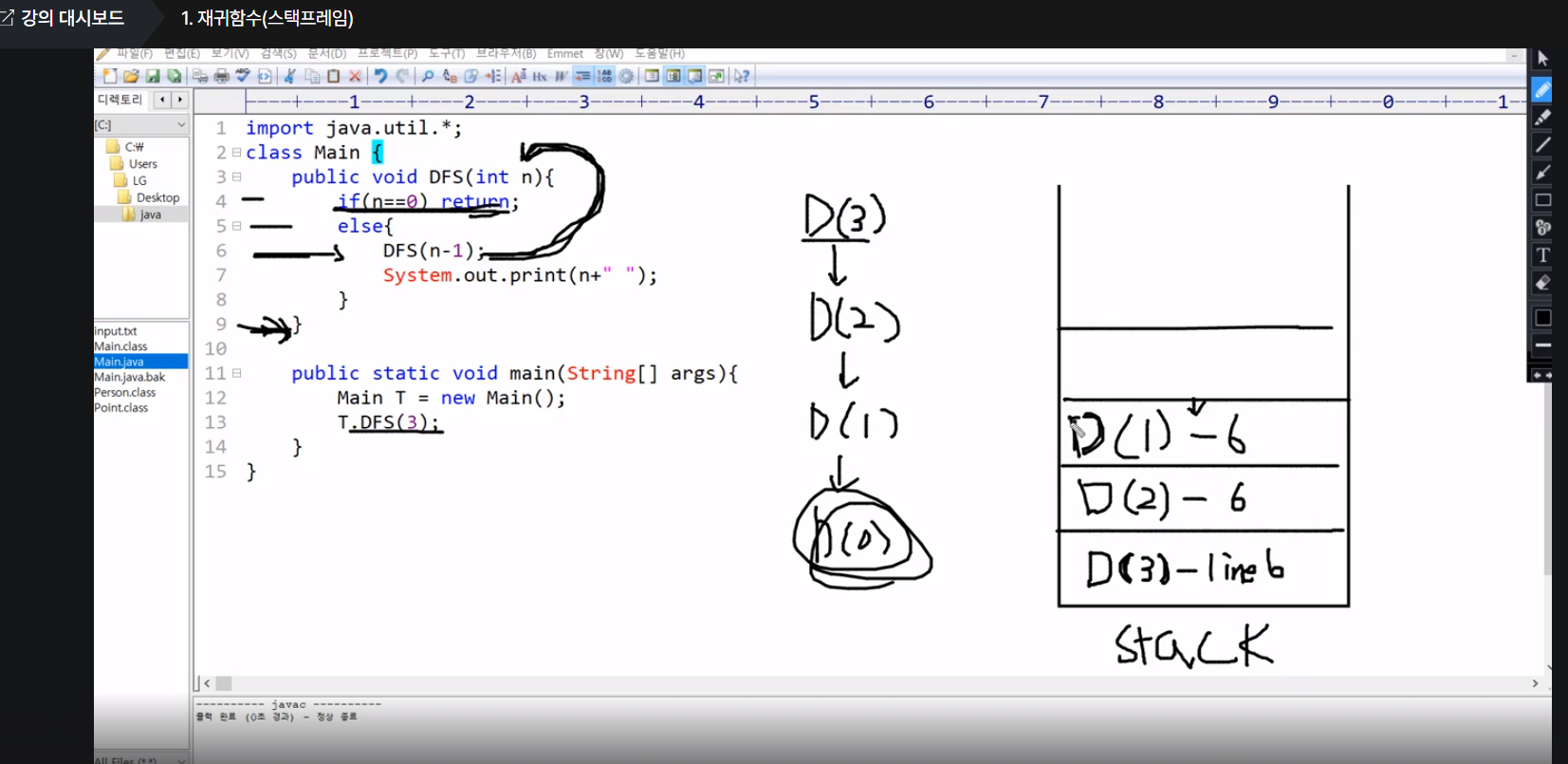
[DFS] - 인프런 자바 입문 - Section 7-2 이진수출력(재귀)
import java.util.*;
public class BinaryPrint {
public void DFS(int n){
if(n==0) return;
else{
DFS(n/2);
System.out.print(n%2+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
BinaryPrint T = new BinaryPrint();
T.DFS(11);
}
}
[DFS] - 인프런 자바 입문 - Section 7-3 팩토리얼
import java.util.*;
public class Factorial {
public int DFS(int n){
if(n==1) return 1;
else return n*DFS(n-1);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Factorial T = new Factorial();
System.out.println(T.DFS(5));
}
}
[DFS] - 인프런 자바 입문 - Section 7-4 피보나치
import java.util.*;
public class Pivonachi {
public int DFS(int n){
if(n==1) return 1;
else if(n==2) return 1;
else return DFS(n-2)+DFS(n-1);
}
public static void main(String [] args){
Pivonachi T = new Pivonachi();
int n=7;
System.out.println(T.DFS(n));
}
}
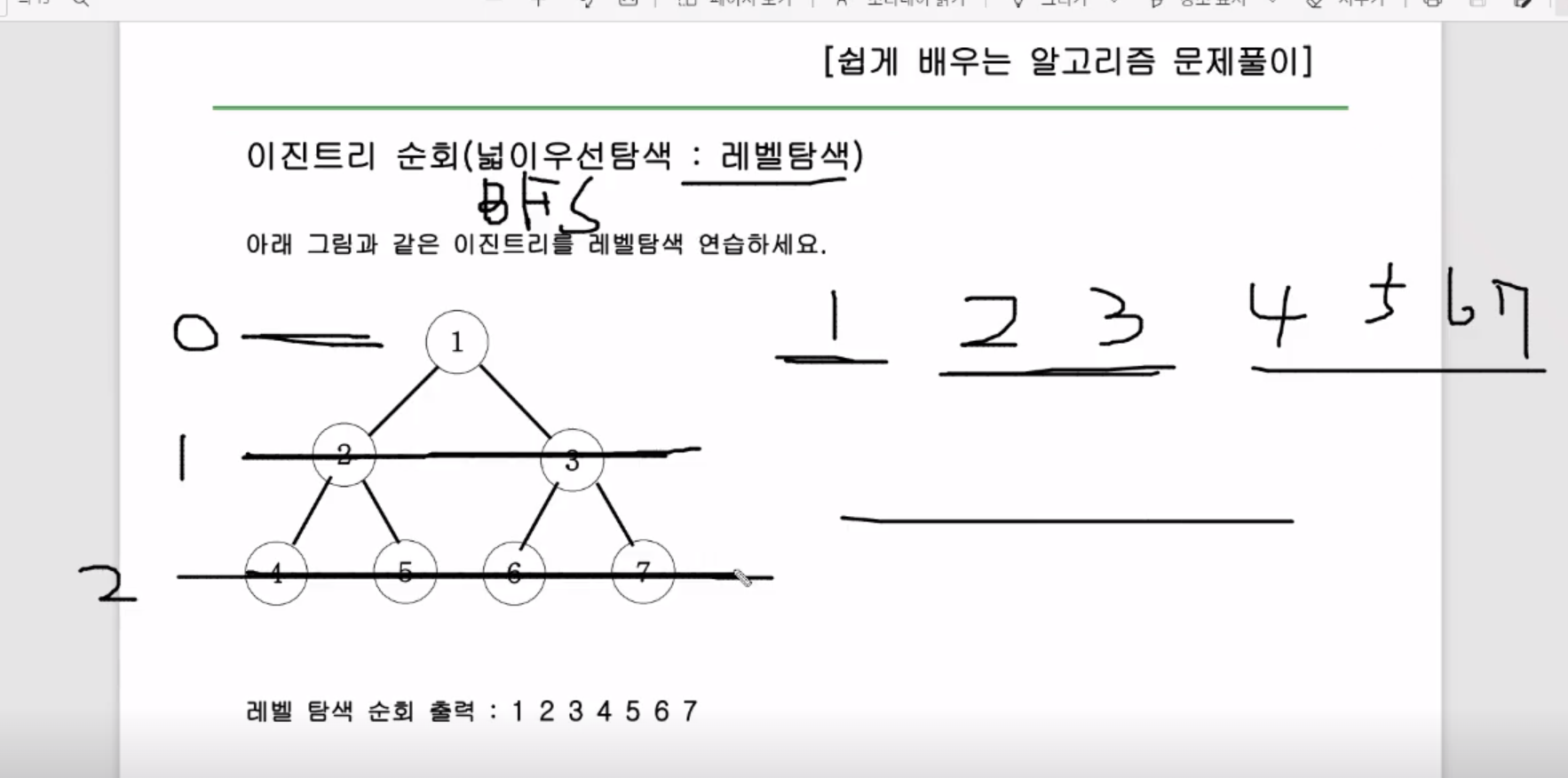
[DFS] - 인프런 자바 입문 - Section 7-5 이진트리순회
[DFS] - 인프런 자바 입문 - Section 7-5 이진트리순회
import java.util.*;
class Node{
int data;
Node lt, rt;
public Node(int val){
data=val;
lt=rt=null;
}
}
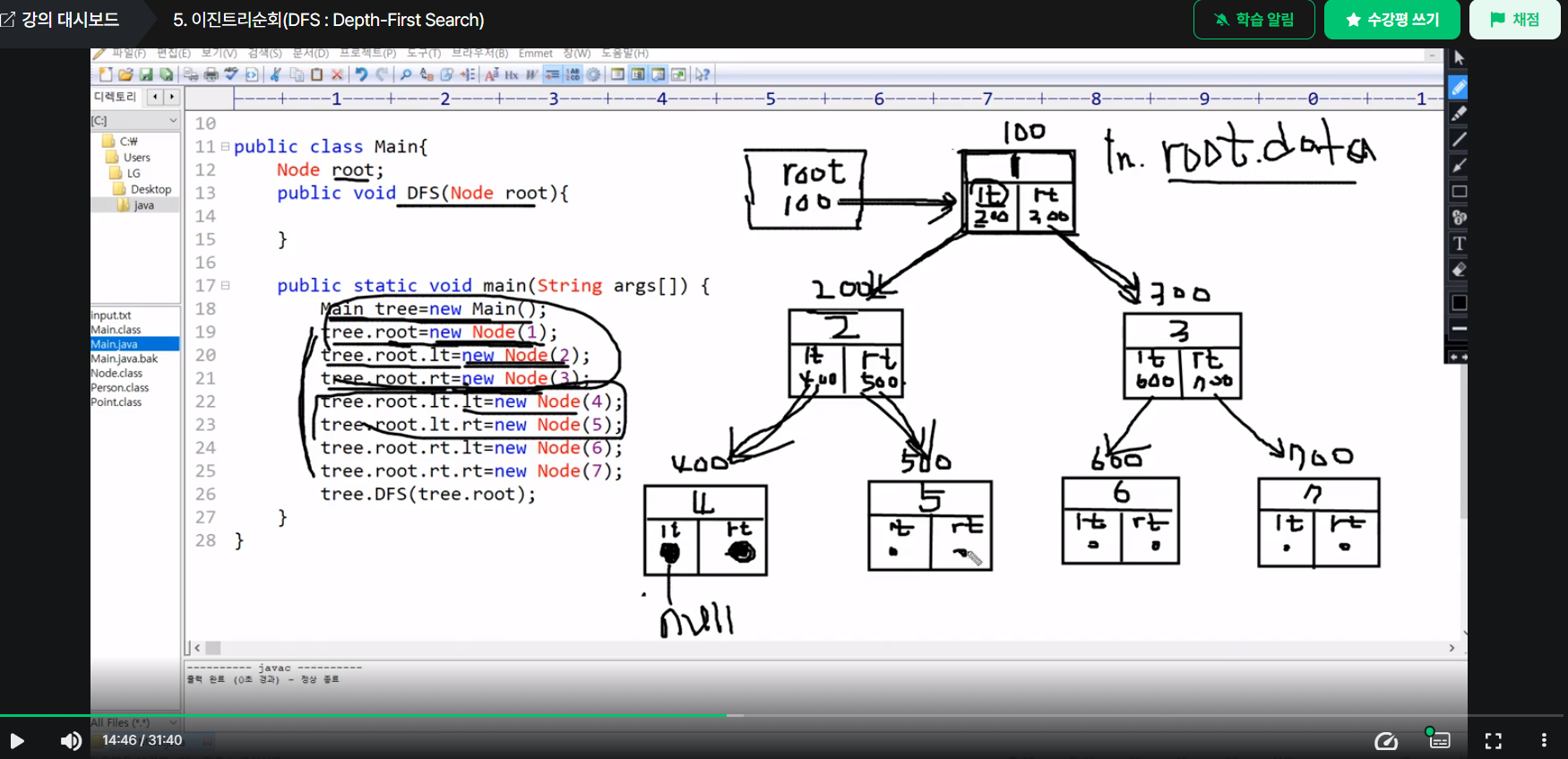
public class Main {
Node root;
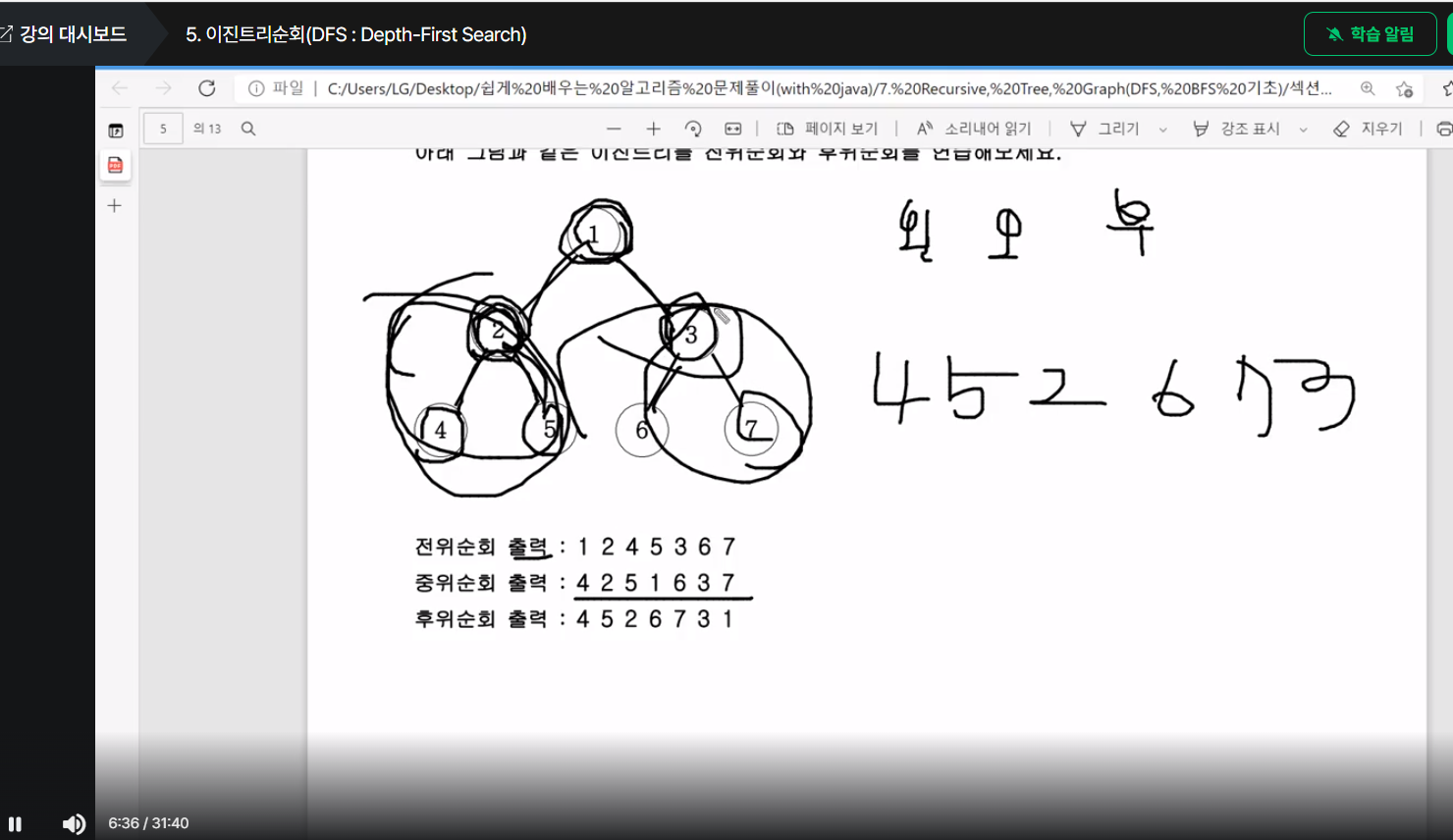
public void DFS(Node root){
if(root==null) return;
else{
DFS(root.lt);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
DFS(root.rt);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Main tree = new Main();
tree.root=new Node(1);
tree.root.lt=new Node(2);
tree.root.rt=new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt=new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.rt=new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt=new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.rt=new Node(7);
tree.DFS(tree.root);
}
}
여기서 root.data를 print하는 구문을 어디 쓰냐에 따라 전위, 중위, 후위 순회가 결정된다 (예시는 중위)
[DFS] - 인프런 자바 입문 - Section 7-6 부분집합
import java.util.*;
public class Subset {
static int n;
static int[] ch;
public void DFS(int L) {
if (L == n + 1) { // 비교 연산자로 수정
String tmp = "";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (ch[i] == 1)
tmp += (i + " ");
}
if (tmp.length() > 0)
System.out.println(tmp);
} else {
ch[L] = 1;
DFS(L + 1);
ch[L] = 0;
DFS(L + 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subset T = new Subset();
n = 3;
ch = new int[n + 1]; // 배열 크기 초기화
T.DFS(1);
}
}
'취업준비 - 코테 , 면접 > 알고리즘(코테) 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DFS (0) | 2024.07.26 |
|---|---|
| 정렬 (0) | 2024.07.26 |
| 실전편 > [5.greedy(탐욕법)] > 5.전투게임 (0) | 2023.08.27 |
| 실전편 > [5.greedy(탐욕법)] > 1.침몰하는 타이타닉 (0) | 2023.08.15 |
| 실전편 > [4.Sorting & Thinking] > 6.멀티태스킹 (0) | 2023.07.11 |


